Automation has become an integral part of modern businesses, streamlining processes and improving efficiency. However, the term “automation” can be misleading, as it encompasses a wide range of techniques and technologies. Understanding the distinctions between Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Automation, and Intelligent Automation is crucial for businesses looking to leverage these tools effectively.
In this blog, we will explore the definitions and key characteristics of RPA, Automation, and Intelligent Automation. We will delve into their benefits, limitations, and real-world applications, helping you make informed decisions about which approach is best suited to your organization’s needs.
RPA: Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation, is a technology that utilizes software robots to mimic human actions and automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. These software robots, often referred to as “bots,” can interact with applications, systems, and data to perform tasks such as:
- Data entry: Automatically entering data into various systems and applications
- Data extraction: Extracting data from different sources and formats
- Data migration: Transferring data from one system to another
- Transaction processing: Handling routine transactions, such as processing orders or invoices
- Form filling: Filling out forms and applications with predefined data
RPA bots are typically configured to follow predefined rules and workflows, making them ideal for automating tasks that are repetitive, structured, and involve minimal decision-making.
59% of the GBS organizations surveyed by Deloitte, RPA is a key transformation technology, making it the most desirable digital enabler.
Benefits of RPA
- Increased efficiency: RPA can automate time-consuming tasks, freeing up employees to focus on strategic & value-added work.
- Improved accuracy: RPA reduces human error by eliminating manual data entry and processing tasks.
- Cost savings: By automating tasks, businesses can reduce labor costs and increase operational efficiency.
- Scalability: RPA bots can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing business demands.
- Faster turnaround times: RPA can accelerate processes, leading to quicker response times and improved customer satisfaction.
Use Cases and Applications
- Finance and accounting: Accounts payable, accounts receivable, expense reporting, reconciliation
- Human resources: Onboarding, payroll processing, benefits administration
- Customer service: Order processing, customer inquiries, claims processing
- IT operations: System maintenance, software deployment, help desk support
- Supply chain management: Inventory management, procurement, logistics
- Legal: Document review, contract management
Limitations of RPA
- Rule-based limitations: RPA is best suited for tasks that follow predefined rules and do not involve complex decision-making.
- Lack of cognitive abilities: RPA bots cannot understand context or reason like humans, limiting their ability to handle unstructured data or adapt to changing circumstances.
- Dependency on existing systems: RPA is dependent on the stability and reliability of the underlying systems and applications.
In summary, RPA is a valuable tool for automating repetitive, rule-based tasks and improving efficiency. However, it is important to understand its limitations and consider whether it is the right solution for your specific needs.
Automation: A Broader Perspective
While RPA focuses on automating specific tasks within existing systems, automation is a broader term that encompasses a wide range of techniques and technologies used to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. Automation can be classified into several types:
- Manual automation: This involves using tools and techniques to simplify manual tasks, such as using spreadsheets or databases to organize information.
- Software-based automation: This involves using software applications to automate various processes, including RPA, workflow automation, and business process management (BPM).
- Automated systems: This refers to systems that can operate independently, without human intervention, such as automated manufacturing lines or self-driving cars.
According to Deloitte, 56% of global business services (GBS) organizations have already implemented RPA and automation and another 33% plan to implement it.
Advantages of automation:
- Improved efficiency: Automation can streamline processes, reduce manual labor, and increase productivity.
- Cost savings: By eliminating manual tasks, businesses can reduce labor costs and improve operational efficiency.
- Increased accuracy: Automation can reduce human error and ensure consistency in data processing.
- Faster turnaround times: Automation can accelerate processes, leading to quicker response times and improved customer satisfaction.
Disadvantages of automation:
- Initial investment: Implementing automation solutions can require significant upfront costs.
- Job displacement: Automation can lead to job losses in certain industries or roles.
- Dependency on technology: Businesses that rely heavily on automation may be vulnerable to technological failures or disruptions.
Automation in various industries:
- Manufacturing: Automated assembly lines, robotics, quality control systems
- Healthcare: Electronic health records, medical imaging analysis, drug discovery
- Finance: Algorithmic trading, risk management, fraud detection
- Transportation: Self-driving cars, automated traffic management systems
- Customer service: Chatbots, automated phone systems
Automation is a pervasive force in today’s world, impacting a wide range of industries and businesses. By understanding the different types of automation and their potential benefits and drawbacks, organizations can make informed decisions about how to leverage automation to improve their operations and achieve their goals.
Intelligent Automation: The Next Level
Intelligent Automation is a more advanced form of automation that combines RPA with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies. By incorporating AI and ML, intelligent automation systems can:
- Understand context: AI and ML algorithms can analyze data and understand the context of tasks, enabling them to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Make decisions: Intelligent automation systems can use AI to make decisions based on data and rules, reducing the need for human intervention.
- Learn and improve: ML algorithms can learn from experience and improve their performance over time.
Intelligent automation software can automate complex document-based workflows, including unstructured data like emails, PDFs, and Word documents. -Indico Data
Benefits of Intelligent Automation:
- Enhanced decision-making: Intelligent automation can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on data analysis.
- Increased flexibility: AI and ML enable intelligent automation systems to handle more complex and unstructured tasks.
- Improved customer experience: Intelligent automation can provide personalized and efficient customer service.
- Continuous improvement: ML algorithms can learn from data and continuously improve the performance of intelligent automation systems.
Use Cases and Applications:
- Natural language processing: Chatbots, virtual assistants, sentiment analysis
- Computer vision: Image recognition, object detection, quality control
- Predictive analytics: Forecasting, risk assessment, customer churn prediction
- Cognitive automation: Knowledge management, process optimization, decision support
Comparison to RPA and Traditional Automation:
- Scope: Intelligent automation is more comprehensive than RPA, as it incorporates AI and ML capabilities.
- Complexity: Intelligent automation can handle more complex and unstructured tasks than traditional automation.
- Learning and adaptation: Intelligent automation systems can learn and adapt to changing circumstances, while traditional automation systems are more rigid.
Intelligent Automation represents the future of automation, offering businesses the potential to achieve significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction. By combining the power of RPA, AI, and ML, Intelligent Automation Systems can automate a wider range of tasks and deliver more advanced capabilities.
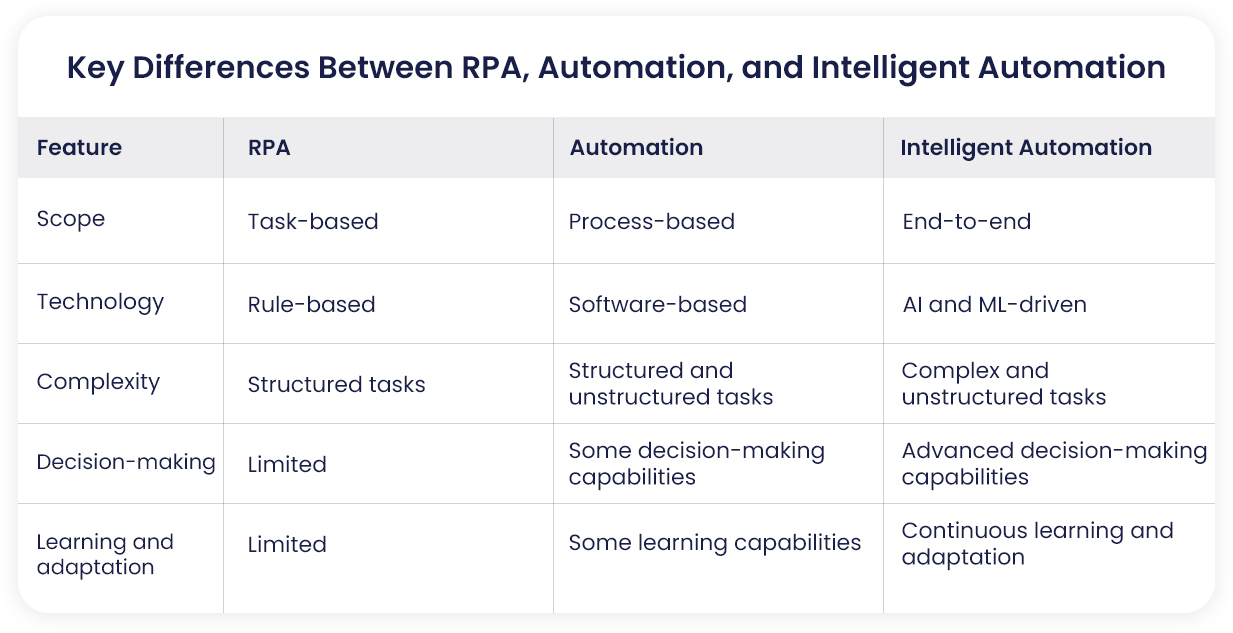
In-depth analysis of the distinctions:
- Scope: RPA focuses on automating specific tasks, while automation encompasses a broader range of activities. Intelligent automation goes beyond tasks and processes, aiming to automate entire end-to-end business operations.
- Technology: RPA relies on rules and workflows, while automation often involves software applications. Intelligent automation leverages AI and ML technologies to enable more complex and adaptive capabilities.
- Complexity: RPA is best suited for structured tasks, while automation can handle both structured and unstructured tasks. Intelligent automation can tackle complex and unstructured tasks that require advanced decision-making and learning capabilities.
- Decision-making: RPA has limited decision-making capabilities, while automation can make some decisions based on predefined rules. Intelligent automation systems can make more complex decisions and adapt to changing circumstances.
- Learning and adaptation: RPA and traditional automation have limited learning and adaptation capabilities. Intelligent automation systems can continuously learn from data and improve their performance over time.
By understanding these key differences, businesses can choose the most appropriate approach for their specific needs and goals.
Choosing the Right Approach: A Decision Framework
When selecting between RPA, automation, or intelligent automation, several factors should be considered:
- Task complexity: Assess the complexity of the tasks you want to automate. RPA is well-suited for structured tasks, while intelligent automation is better equipped for complex and unstructured tasks.
- Data structure: Consider the structure of the data involved. RPA works well with structured data, while intelligent automation can handle unstructured data more effectively.
- Decision-making requirements: Determine the level of decision-making required for the tasks. RPA is limited in decision-making capabilities, while intelligent automation can make more complex decisions.
- Scalability: Evaluate your future needs and consider how the automation solution can scale to accommodate growth.
- Cost and ROI: Analyze the costs associated with each approach and assess the potential return on investment.
- Existing systems and infrastructure: Evaluate the compatibility of the automation solution with your current systems and infrastructure.
Potential hybrid approaches:
- RPA and automation: Combine RPA with other automation technologies to automate a wider range of processes.
- RPA and intelligent automation: Integrate RPA with AI and ML capabilities to enhance decision-making and adaptability.
- Automation and intelligent automation: Leverage a combination of automation techniques and intelligent automation to address different types of tasks.
By carefully considering these factors and evaluating your specific needs, you can choose the most appropriate automation approach to drive efficiency, productivity, and innovation within your organization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, RPA, automation, and intelligent automation are distinct approaches to automating tasks and processes. RPA is well-suited for structured, rule-based tasks, while automation encompasses a broader range of techniques and technologies. Intelligent automation, powered by AI and ML, offers advanced capabilities for handling complex and unstructured tasks.
By understanding the key differences between these approaches and considering your specific needs, you can make informed decisions about which automation solution is best for your organization. As technology continues to evolve, it is likely that intelligent automation will play an increasingly important role in driving efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage.
At Charter Global, we specialize in providing comprehensive automation solutions tailored to your unique requirements. Our team of experts can help you assess your needs, select the most appropriate automation approach, and implement and manage your automation initiatives. Are you ready to realize it’s full potential?
Contact us today.
Or mail us at [email protected] or call +1 770 326 9933

